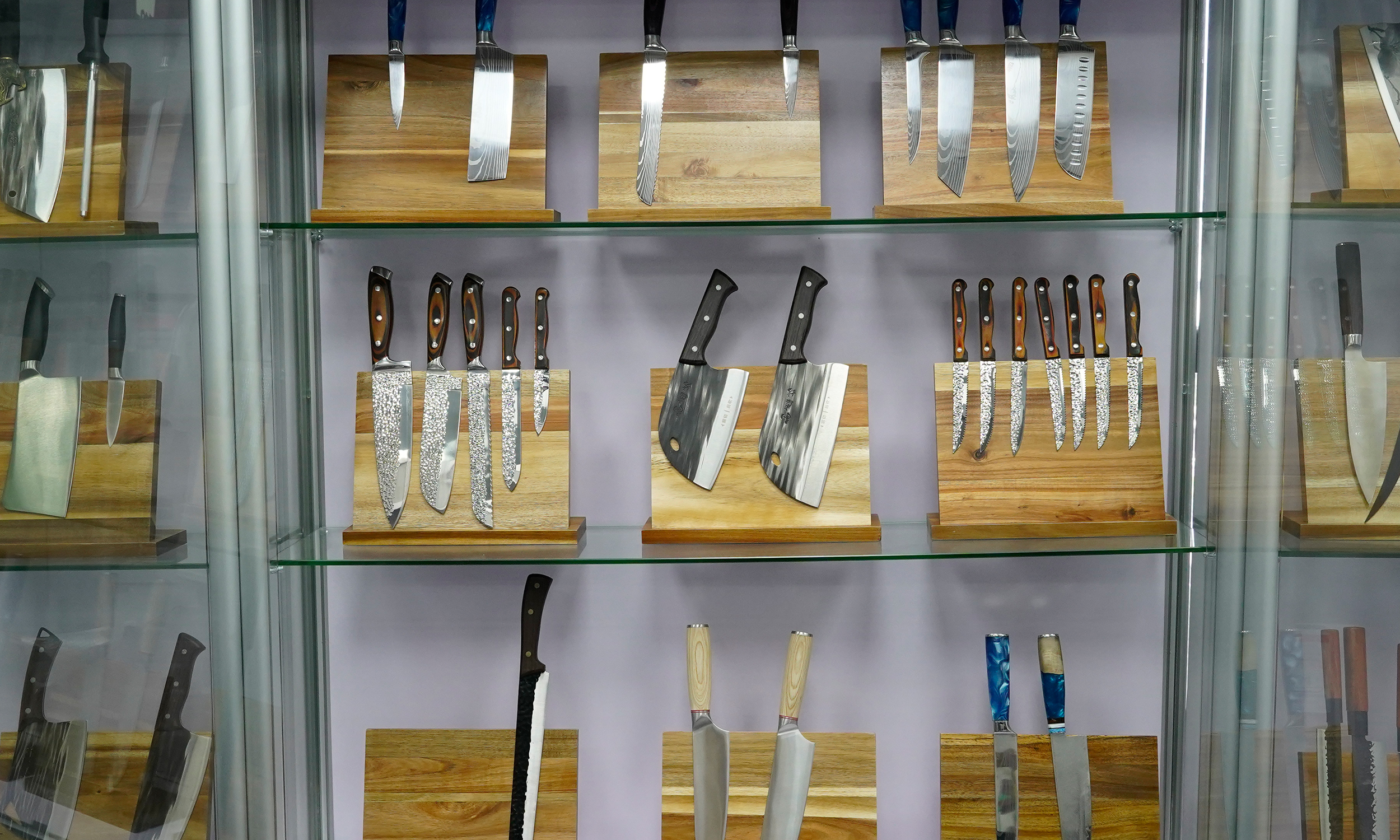
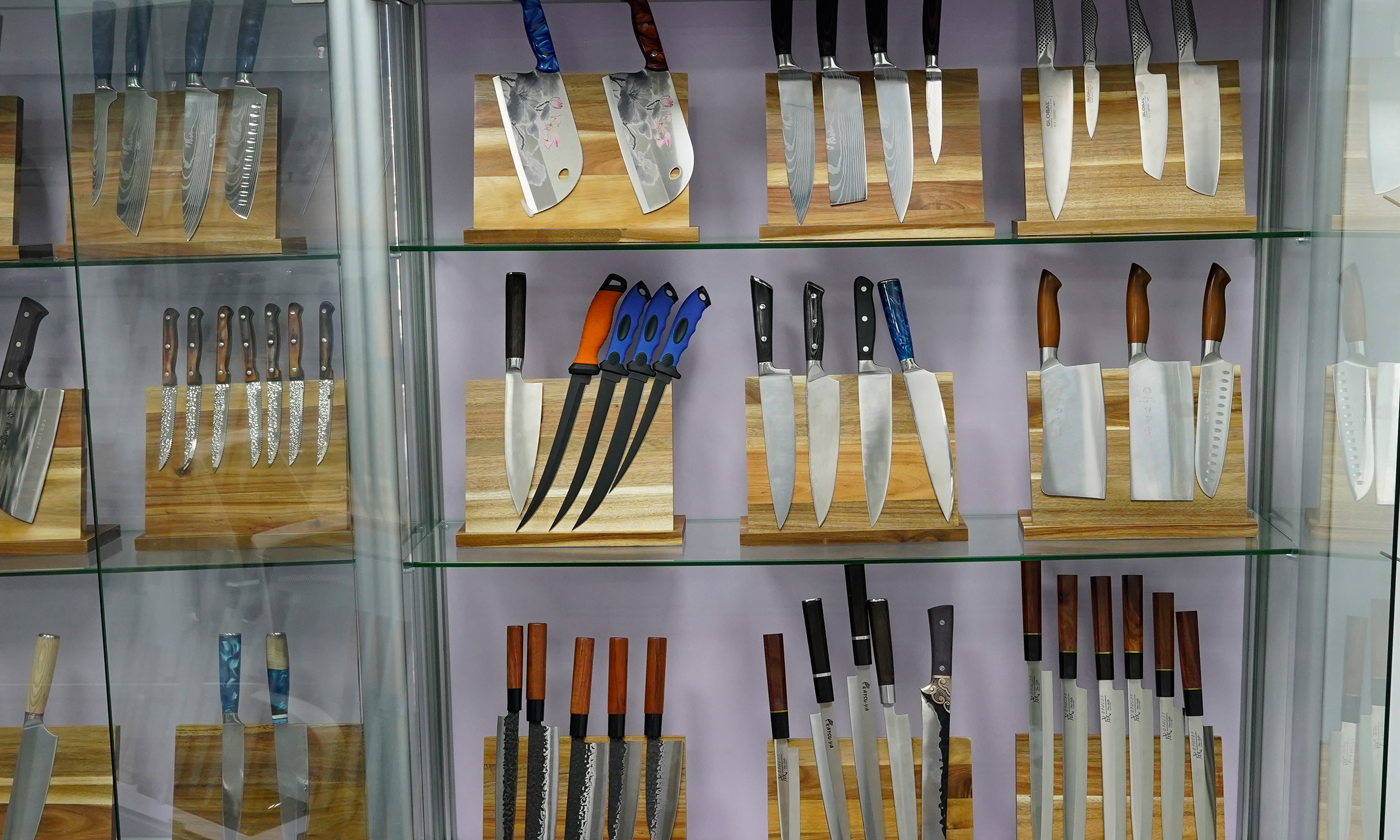
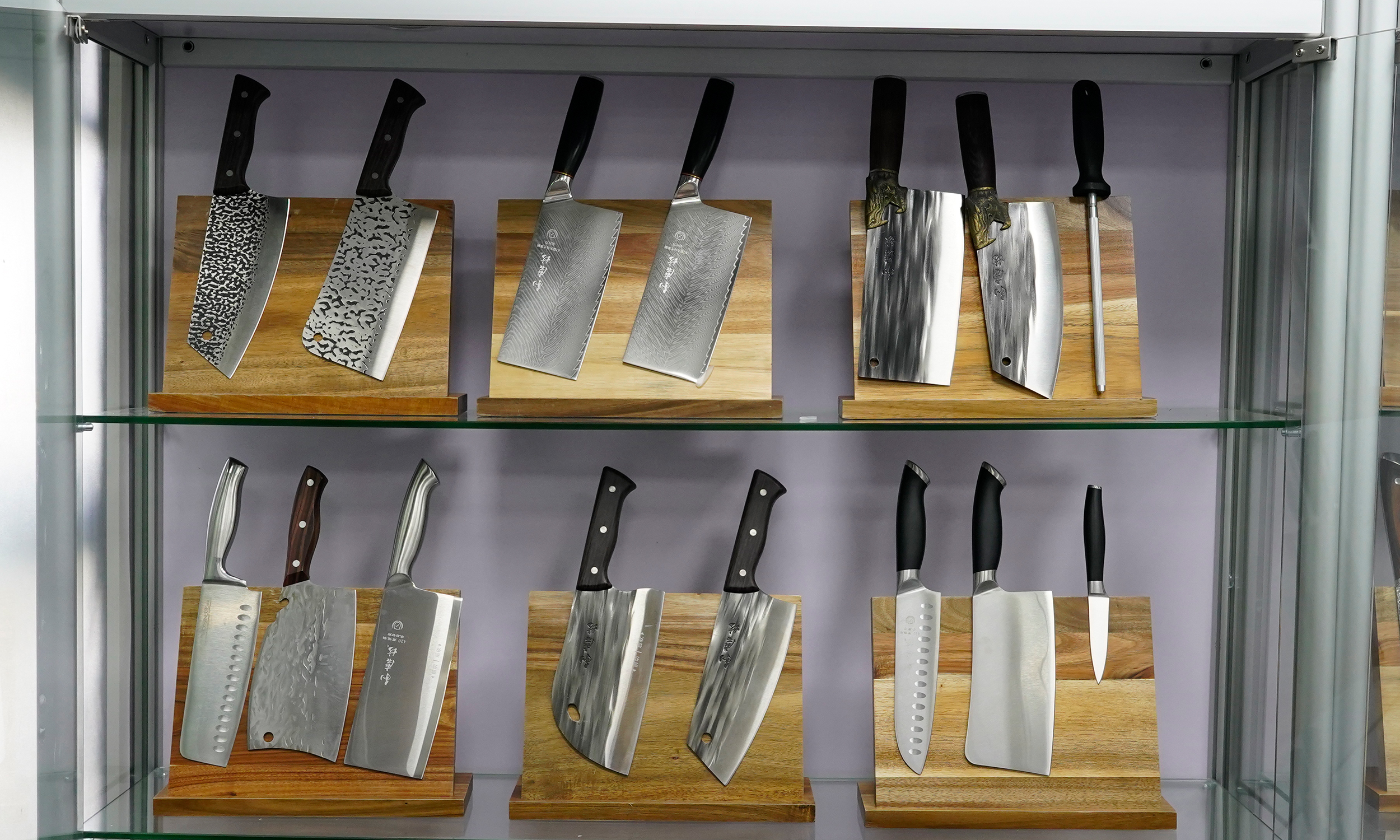
Western kitchen knives are renowned for their diverse craftsmanship, which not only determines the knife’s performance but also affects its appearance and durability. From traditional forging techniques to modern laser cutting methods, each type of craftsmanship offers unique features and advantages. This article explores the main types of craftsmanship in Western kitchen knives and examines how these techniques impact the knife’s performance and user experience.
1. Forging Craftsmanship
Forging is one of the oldest and most classic techniques for making Western kitchen knives. This process involves heating the metal to a high temperature and then shaping it by hammering or mechanical pressure. The key features of forging include:
- Durability: Forging creates a uniform metal grain structure, enhancing the strength and durability of the knife.
- Sharpness: The uniformity achieved through forging helps maintain the knife’s sharpness and makes it easier to sharpen and maintain.
- Integral Design: Many high-quality forged knives feature an integral design, where the blade and handle are continuous, providing better balance and durability.
2. Cold Forging
Cold forging is a more modern technique compared to hot forging. Unlike hot forging, cold forging is performed at room temperature, using pressure to shape the metal into the knife’s form. The main characteristics of cold forging are:
- High Precision: Cold forging allows for precise control over the knife’s shape and dimensions, resulting in a more refined appearance.
- Increased Hardness: Cold-forged knives typically exhibit higher hardness and wear resistance.
- Reduced Heat Treatment Needs: Since cold forging does not involve high temperatures, the need for subsequent heat treatment is reduced, minimizing potential deformation.
3.Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a modern technique that uses laser beams to precisely cut the shape of the knife. This method is particularly useful for producing complex shapes and patterns. The advantages of laser cutting include:
- Precision Cutting: Laser cutting achieves extremely high accuracy, ensuring consistent and symmetrical knife shapes.
- Complex Designs: Ideal for creating intricate blade designs or patterns.
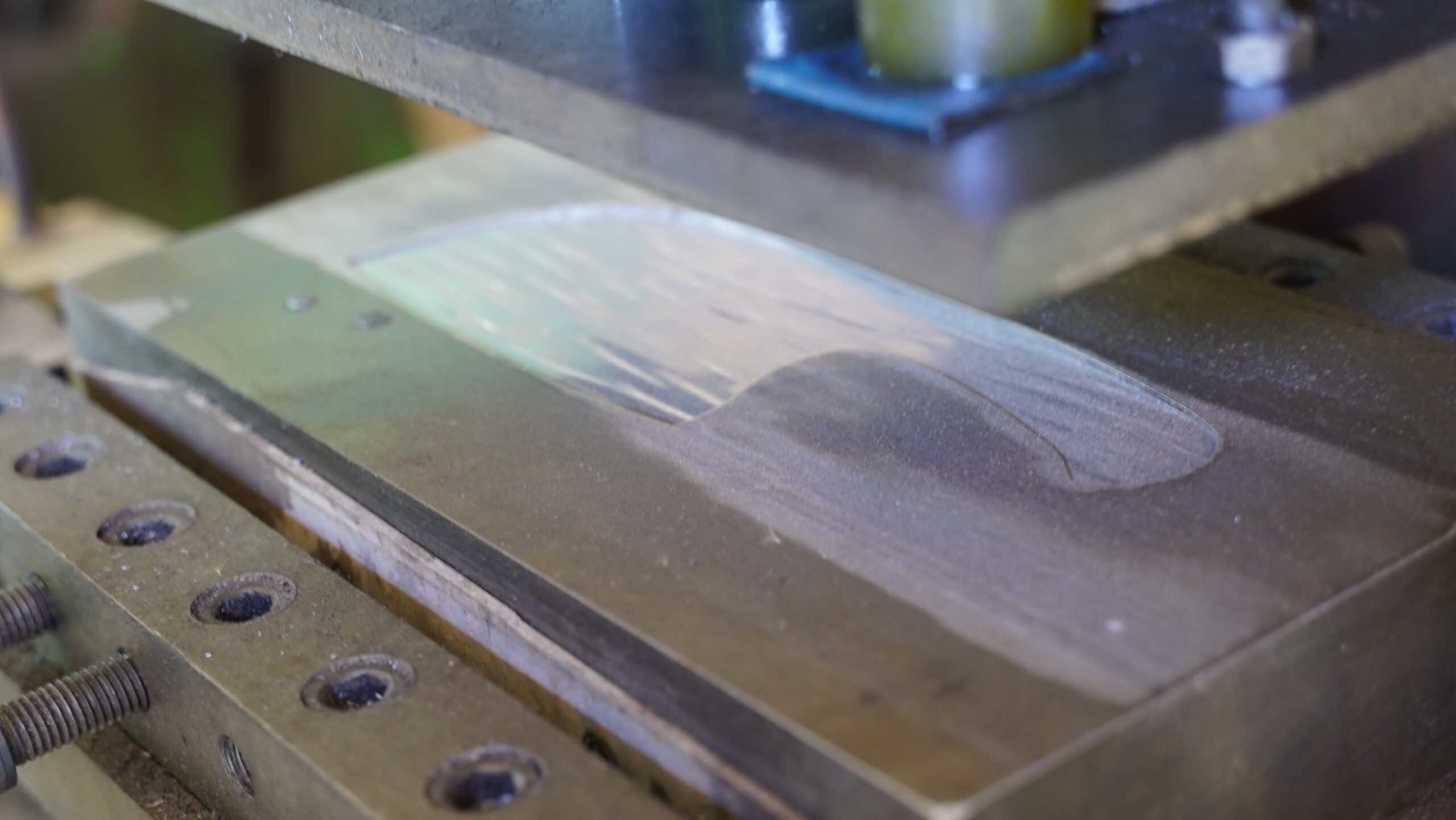

- Efficient Production: Laser cutting significantly boosts production efficiency, shortening manufacturing cycles.
4. Electroplating
Electroplating is a technique that deposits a layer of metal onto the knife’s surface through an electrochemical process. The features of electroplating include:
- Corrosion Resistance: The plating layer effectively prevents rust and extends the knife’s lifespan.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Electroplating can enhance the knife’s appearance with added gloss and color.
- Wear Resistance: The plating increases the hardness of the knife’s surface, reducing wear and scratches.
5. Grinding
Grinding is a process used to refine the knife’s edge after its basic shape has been formed. Grinding techniques include:
- Hand Grinding: Performed by skilled artisans, allowing for detailed adjustments to ensure optimal sharpness and uniformity.
- Machine Grinding: Uses grinding machines for mass production, improving efficiency and consistency.
- Multi-Stage Grinding: Typically involves coarse grinding, fine grinding, and polishing to achieve the best cutting performance and appearance.
6. Casting
Casting is a technique where molten metal is poured into molds to form the basic shape of the knife. The characteristics of casting include:
- Design Flexibility: Suitable for producing knives with complex shapes or special designs.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces production costs for large quantities.
- Surface Finishing: Cast knives often require additional grinding and polishing to meet final quality standards.
7. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment involves heating and cooling the knife to enhance its properties. Common heat treatment processes include:
- Quenching: Heating the knife to high temperatures and then rapidly cooling it to increase hardness.
- Tempering: Heating the quenched knife to improve toughness and reduce brittleness.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling the knife to improve its workability and toughness.
8. Sample Display
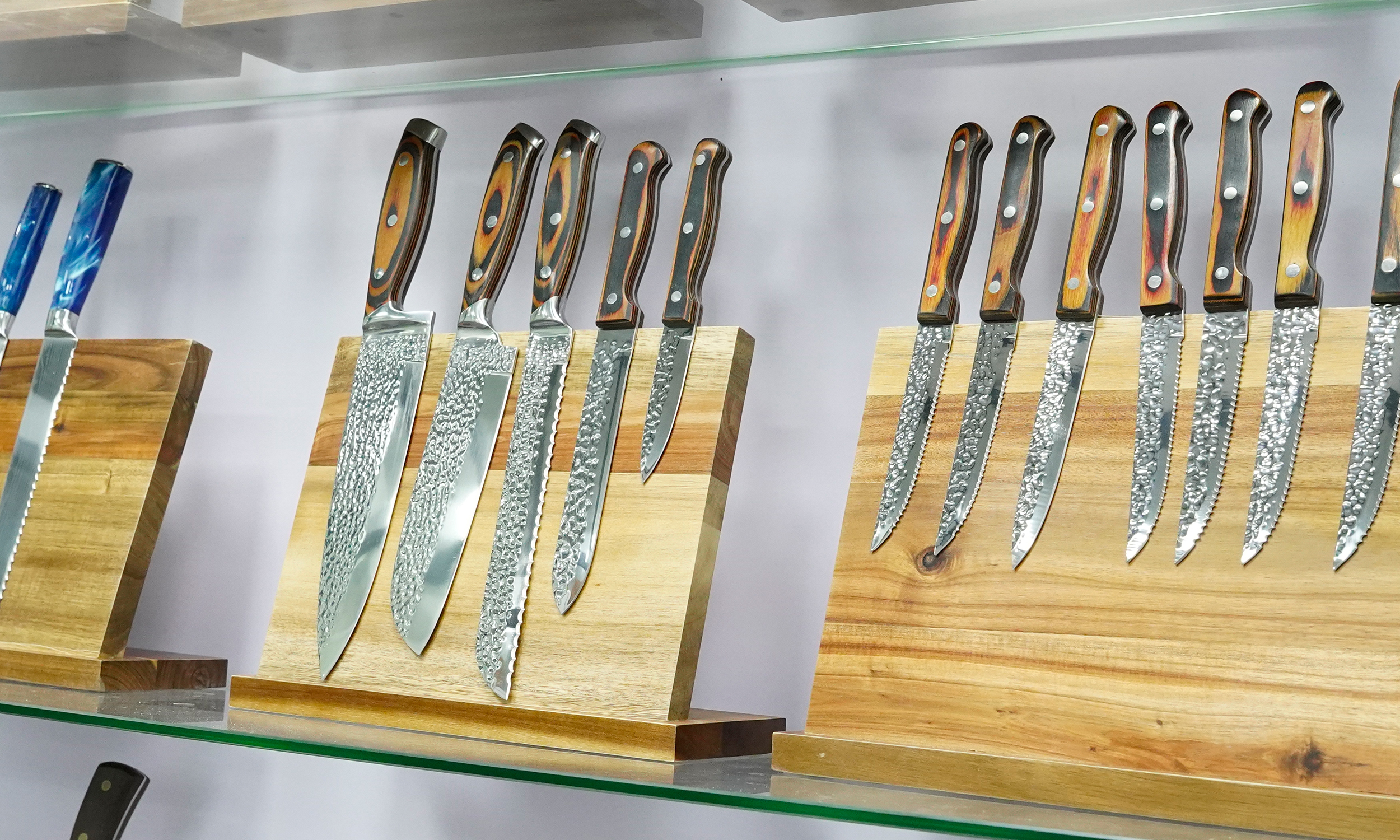

Conclusion
The craftsmanship of Western kitchen knives is rich and varied, from traditional forging to modern laser cutting. Each type of craftsmanship offers distinct advantages and is suited to different knife functions and user preferences. Understanding these craftsmanship types not only helps in selecting the right kitchen knife but also enhances appreciation and maintenance of this essential culinary tool.
 Yangjiang 안토니 나이프 Co., 주식 회사
Yangjiang 안토니 나이프 Co., 주식 회사 

